Cold Storage Warehouses Role, Benefits, and Real-World Use Cases Explained
Cold storage warehouses are specialized facilities designed to preserve temperature-sensitive goods such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. Unlike conventional warehouses, they use advanced refrigeration systems to maintain controlled environments that prevent spoilage, maintain quality, and extend shelf life.
These facilities are a critical part of the global supply chain, ensuring that perishable goods move safely from producers to consumers. With the rise of global trade, e-commerce grocery delivery, and pharmaceutical distribution, cold storage warehouses have become indispensable in ensuring food security, healthcare reliability, and consumer satisfaction.
Importance of Cold Storage in Supply Chains
Cold storage warehouses are essential for industries that depend on product integrity. For the food industry, they ensure that meat, dairy, frozen goods, and fresh produce remain safe for consumption during storage and transit. In pharmaceuticals, they safeguard sensitive products such as vaccines, insulin, and biologics, which require strict temperature conditions.
Without cold storage facilities, businesses risk losing products to spoilage, contamination, or reduced potency. This would lead to financial losses, regulatory issues, and consumer dissatisfaction. By integrating cold storage warehouses into supply chains, businesses maintain quality assurance, reduce waste, and comply with industry standards.
Benefits of Cold Storage Warehouses
The primary benefit of cold storage warehouses is extended product shelf life. By maintaining products at precise temperatures, businesses reduce spoilage and waste, maximizing profitability. This is particularly important in industries such as retail and pharmaceuticals, where margins can be impacted heavily by losses.
Another major benefit is regulatory compliance. Many industries face strict storage and handling requirements. Cold storage warehouses ensure compliance with health and safety regulations, protecting businesses from penalties and recalls.
Additionally, cold storage provides market expansion opportunities. Businesses can ship products to distant markets without compromising quality, opening new sales channels, and increasing competitiveness in international trade.
Real-World Examples of Cold Storage Warehouses
1. Lineage Logistics Facilities
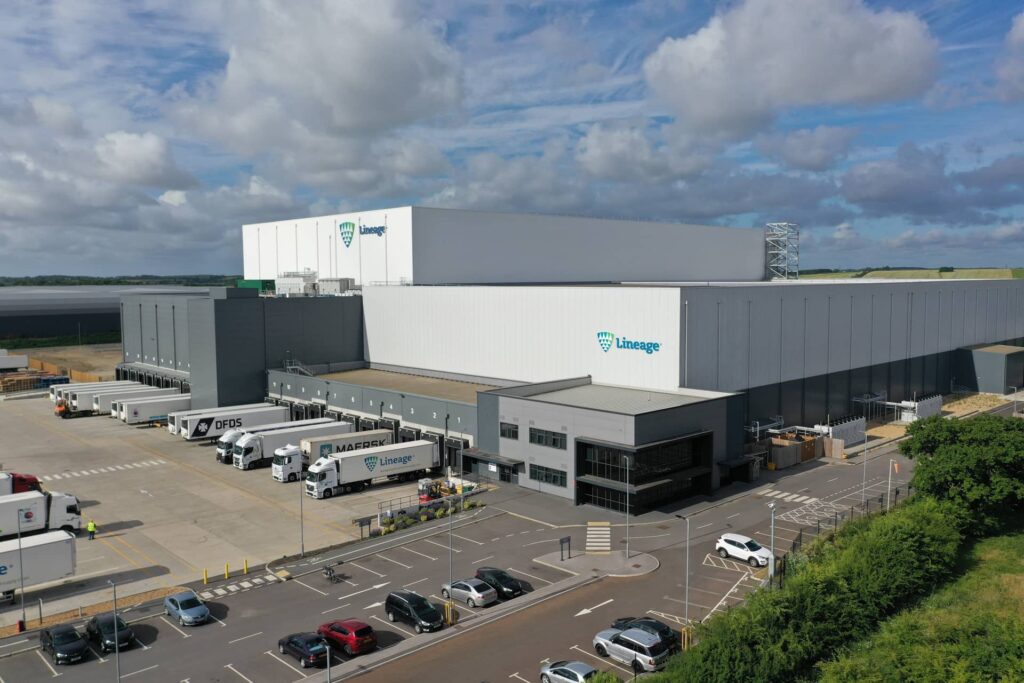

Lineage Logistics operates one of the largest networks of cold storage warehouses worldwide. Their facilities are equipped with advanced automation, energy-efficient refrigeration, and data-driven monitoring systems.
The relevance of Lineage’s operations lies in scale and innovation. They enable global retailers, food producers, and distributors to store and ship products safely across continents. By combining advanced technology with vast infrastructure, Lineage sets industry standards for reliability and efficiency in cold storage.
2. Americold Cold Storage Warehouses
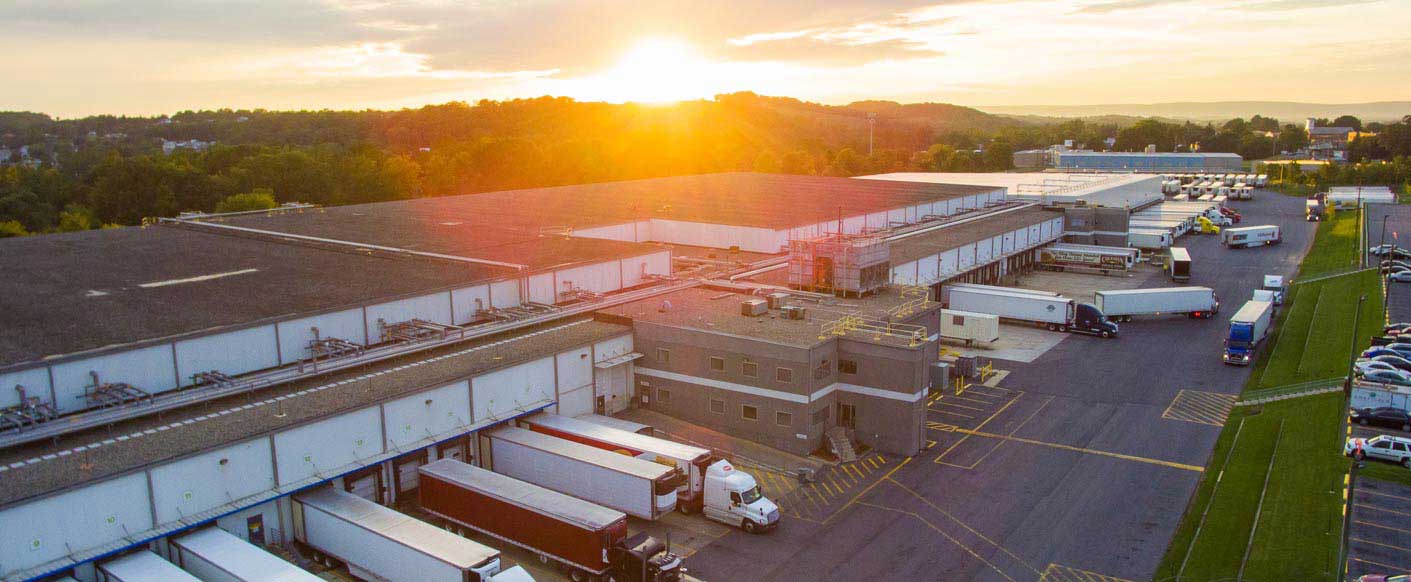

Americold is another global leader specializing in temperature-controlled warehousing. Their facilities are strategically located near food production areas, ports, and major cities, ensuring quick access to both suppliers and consumers.
The relevance of Americold’s model is in strategic positioning. Their locations minimize transit times, which is crucial for perishable goods. Additionally, Americold integrates advanced warehouse management systems that allow real-time tracking of inventory, ensuring customers have full visibility into their supply chains.
3. United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Cold Storage Facilities

The USDA operates cold storage warehouses to support national food security and supply management. These facilities store surplus food and ensure a stable supply during emergencies or shortages.
The relevance of this example is in public sector support. By maintaining cold storage infrastructure, governments play a key role in stabilizing markets and ensuring food availability. These warehouses also highlight how cold storage goes beyond business, serving as a strategic resource for national resilience.
4. Pharmaceutical Cold Storage by DHL
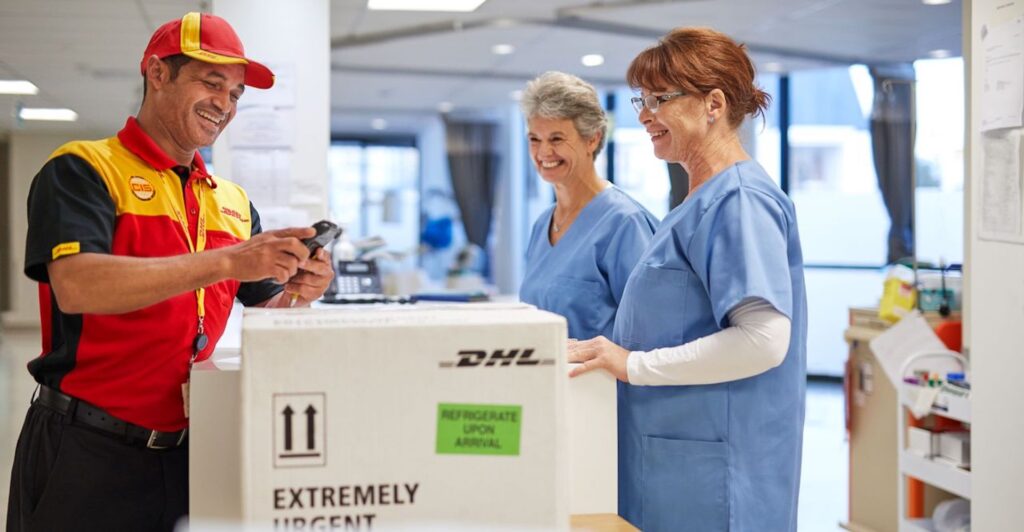

DHL has invested heavily in pharmaceutical cold storage facilities worldwide. These warehouses are designed to handle sensitive medicines, vaccines, and biologics under strict temperature conditions ranging from frozen to ambient-controlled environments.
The relevance of DHL’s facilities is in healthcare reliability. During the COVID-19 pandemic, their cold storage warehouses played a crucial role in distributing vaccines globally. This demonstrates how cold storage warehouses are vital in addressing urgent global health challenges.
5. Urban Cold Storage for Grocery E-commerce

In major cities, e-commerce companies operate smaller urban hubs to handle fresh and frozen groceries for same-day or next-day delivery. These micro-warehouses are designed for fast throughput and last-mile efficiency.
The relevance of this trend is in consumer convenience. As online grocery shopping becomes mainstream, urban cold storage ensures perishable products reach customers quickly while maintaining freshness. This new model demonstrates the growing integration of cold storage into everyday consumer experiences.
Use Cases of Cold Storage Warehouses
Solve multiple real-world business problems. In agriculture, they prevent post-harvest losses by storing crops like fruits and vegetables until they are ready for market. Farmers benefit from reduced spoilage and improved profitability.
In the seafood industry, cold storage ensures fish and other marine products remain safe during transportation from coastal areas to inland markets. Without these facilities, products would spoil quickly, reducing both availability and affordability.
Pharmaceutical companies rely on cold storage for distributing life-saving medicines. Without temperature control, products like vaccines could lose effectiveness, leading to public health risks. Cold storage warehouses guarantee safety and compliance while enabling global distribution.
How Technology Enhances
Technology is revolutionizing, making them more efficient, reliable, and sustainable. Automation is increasingly being used to improve handling efficiency. Robotic systems perform tasks such as palletizing, picking, and inventory management, reducing reliance on manual labor in freezing conditions.
IoT sensors provide real-time monitoring of temperature, humidity, and air quality. This ensures that products remain within required conditions and alerts operators to any deviations immediately. Advanced warehouse management systems (WMS) also integrate data analytics, enabling predictive maintenance and demand forecasting.
Sustainability is another area where technology plays a role. They are energy-intensive, but innovations such as solar power integration, energy-efficient refrigeration, and smart insulation are reducing carbon footprints. These technologies not only cut costs but also align with environmental regulations and consumer expectations.
Challenges of Cold Storage Warehouses
Despite their importance, they face challenges. One major issue is high operating costs. Maintaining low temperatures requires significant energy consumption, making sustainability and efficiency critical for profitability.
Another challenge is limited capacity. As demand for cold storage increases, particularly from e-commerce and pharmaceuticals, shortages can drive up costs and limit availability. Companies must carefully plan capacity expansions to meet market needs.
Additionally, workforce management in cold environments can be difficult. Working in freezing conditions is physically demanding, requiring special training, equipment, and safety measures.
Future of Cold Storage Warehouses
The future will be shaped by digitalization, automation, and sustainability. Smart facilities that use AI, robotics, and IoT will dominate the market, reducing energy costs and increasing reliability.
Smaller, decentralized cold storage facilities near urban centers will grow in demand due to the rise of e-commerce grocery delivery. Meanwhile, global logistics companies will continue investing in large-scale cold storage hubs to support international food and pharmaceutical distribution.
As consumers demand fresher products and faster deliveries, it will remain central to global supply chain innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is a cold storage warehouse used for?
A cold storage warehouse is used to store temperature-sensitive goods such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. These facilities maintain controlled environments to ensure product quality, safety, and compliance.
Q2. How do cold storage warehouses benefit businesses?
They extend product shelf life, reduce spoilage, ensure regulatory compliance, and open opportunities for businesses to expand into new markets. They also support faster and more reliable supply chains.
Q3. What technologies are used in?
Technologies include automation, robotics, IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and energy-efficient refrigeration systems. These tools improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance sustainability.