Factory Properties for Rent Complete Guide, Benefits, and Real-World Use Cases
Factory properties for rent are specialized industrial spaces designed to accommodate manufacturing, production, warehousing, and logistical operations. Unlike conventional office or retail spaces, these properties are equipped with infrastructure that supports heavy machinery, large-scale operations, and supply chain activities. Renting factory properties provides businesses with access to industrial facilities without the high upfront costs of purchasing land and constructing their own factory.
As global trade expands and industries become more dynamic, demand for flexible and affordable factory rentals continues to rise. Whether for startups in need of small production facilities or large corporations requiring strategic regional hubs, renting factory properties is a practical solution that allows companies to scale operations while managing costs effectively.
Why Businesses Rent Factory Properties
Factory rentals are attractive for businesses because they provide immediate access to industrial infrastructure. Instead of waiting months or years for construction, companies can move into a fully functional space and begin operations quickly. This flexibility is particularly valuable for businesses that need to respond rapidly to market demand.
Additionally, factory rentals reduce financial risk. Purchasing property often requires significant capital investment, while renting allows companies to conserve funds for other critical business activities such as product development, marketing, and hiring. Rental agreements may also include maintenance and utilities, which further reduces operational burdens for tenants.
Types of Factory Properties for Rent
Factory properties vary widely depending on their design and purpose. Some are built for light manufacturing, which involves assembly and packaging operations. Others are designed for heavy manufacturing, capable of housing machinery for automotive production, metal fabrication, or electronics manufacturing.
There are also specialized factory properties that combine production with warehousing and distribution functions. These hybrid spaces allow companies to manufacture goods and distribute them from the same facility, streamlining logistics. Understanding the type of factory property required is essential before committing to a lease, as the facility must match the company’s operational needs.
Benefits of Renting Factory Properties
Renting factory properties provides businesses with several practical advantages. One major benefit is flexibility. Businesses can choose rental terms that align with their growth stage, whether short-term leases for seasonal production or long-term rentals for sustained operations.
Another significant benefit is cost efficiency. Renting eliminates the need for large upfront investments, freeing up cash flow for other priorities. It also reduces exposure to market risks, as companies are not tied to long-term property ownership in areas that may experience economic downturns.
Finally, strategic location is a major advantage. Many factory rentals are situated in industrial zones close to highways, ports, and airports. This proximity to transportation hubs reduces logistics costs and ensures faster delivery times, which is crucial for competitive supply chain management.
Real-World Examples of Factory Properties for Rent
1. Industrial Park Manufacturing Facilities
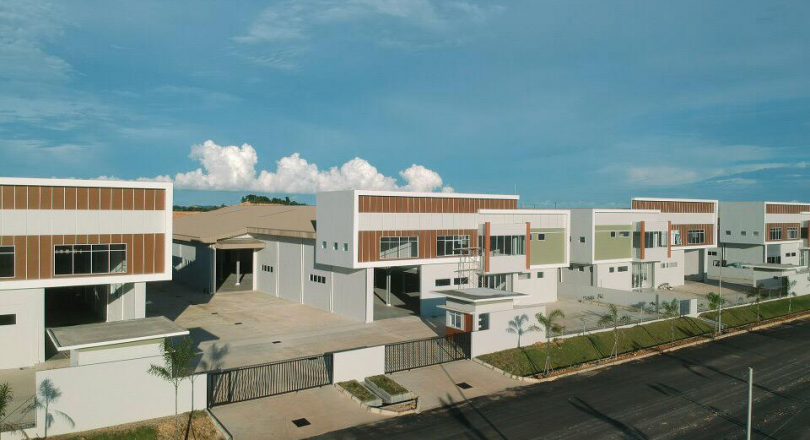

Many industrial parks worldwide offer factory properties for rent. These facilities are designed for multiple tenants, creating business ecosystems where companies can share infrastructure such as security, utilities, and transportation access.
The relevance of this model is in the community effect. Businesses benefit from being near suppliers, partners, and distribution centers, reducing logistics complexity. Startups, in particular, thrive in industrial parks because they gain access to facilities without large capital expenditure while benefiting from shared services.
2. Converted Warehouses for Small-Scale Manufacturing

In urban areas, old warehouses are increasingly being converted into factory spaces for rent. These facilities often cater to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) engaged in crafts, textiles, or light manufacturing.
The relevance of this trend lies in urban accessibility. SMEs that require proximity to city markets can operate efficiently without relocating to remote industrial zones. Converted warehouses also appeal to businesses with sustainability goals, as they make use of existing infrastructure instead of constructing new buildings.
3. Automotive Component Manufacturing Factories
Automotive suppliers often rely on rented factory spaces close to car manufacturers’ assembly plants. These facilities are built to handle large-scale production while meeting strict quality and safety standards.
The relevance of this model is in just-in-time production. Renting factories near automotive plants ensures that suppliers can deliver components quickly and reliably, reducing costs and avoiding production delays. This approach highlights how factory rentals support industries that depend on precision logistics.
4. Tech Manufacturing Facilities in Asia

Countries like Vietnam, Malaysia, and Indonesia have become hotspots for renting factory properties dedicated to electronics and semiconductor production. Global technology companies often lease these facilities to take advantage of favorable labor costs and proximity to global shipping routes.
The relevance of this trend is in scalability and globalization. Renting factories abroad allows companies to expand into new markets without building expensive facilities from scratch. It also demonstrates how multinational corporations leverage factory rentals to remain competitive in global supply chains.
Use Cases of Factory Properties for Rent
Factory rentals are useful in solving several business challenges. For startups, they eliminate the need for significant capital investment, allowing companies to focus on growth while still accessing industrial-grade facilities. Without rentals, many small businesses would be unable to compete in markets that require physical production capacity.
For established businesses, factory rentals solve the problem of seasonal demand fluctuations. Instead of over-investing in permanent facilities, companies can lease additional space during peak seasons. This flexibility ensures businesses remain agile and responsive to changing consumer demand.
Another use case is international expansion. Companies entering new markets often rent factories to test demand before committing to permanent infrastructure. This strategy reduces financial risk and provides valuable insights into regional market dynamics.
How Technology Enhances Factory Properties for Rent
Technology is transforming how factory rentals operate. Smart factory solutions such as IoT (Internet of Things) sensors and AI-driven monitoring systems are increasingly integrated into rental properties. These tools allow businesses to track energy consumption, equipment performance, and environmental conditions in real time.
Automation technologies, including robotics, further enhance efficiency by reducing manual labor requirements. Many modern factory rentals also feature advanced digital infrastructure that supports predictive maintenance, helping tenants avoid costly equipment downtime. By offering these features, landlords make factory rentals more attractive to technology-driven businesses.
Challenges of Renting Factory Properties
While renting factory properties has clear advantages, it also comes with challenges. One common issue is limited customization. Tenants may not be able to modify the facility extensively to suit their operations, which can be a constraint for highly specialized industries.
Another challenge is rental cost variability. Prices depend heavily on location, size, and demand. Businesses must carefully evaluate rental agreements to avoid hidden fees, such as maintenance costs or service charges. Despite these challenges, factory rentals remain a strong option for many businesses due to their flexibility.
Future of Factory Properties for Rent
The future of factory rentals lies in more flexible, technology-enabled, and sustainable facilities. As businesses demand greener operations, landlords are expected to integrate renewable energy sources such as solar power and energy-efficient systems.
Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 will make smart factories more common. Rental properties will increasingly offer digital tools that enhance productivity, creating opportunities for businesses of all sizes to access advanced infrastructure without major investment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the main advantage of renting factory properties?
The main advantage is flexibility. Renting provides access to industrial facilities without heavy capital investment, allowing businesses to scale operations as needed while minimizing financial risk.
Q2. Are factory rentals suitable for small businesses?
Yes. Small and medium-sized enterprises benefit significantly from factory rentals because they gain access to professional-grade infrastructure at affordable costs. This makes it easier for them to compete with larger companies.
Q3. How is technology changing factory rentals?
Technology is making factory rentals smarter and more efficient. IoT sensors, automation, and predictive analytics help businesses optimize production, reduce downtime, and improve overall operational efficiency within rented facilities.